Model Coin Cell Swelling system testing machine for Lab
Introduction
As a popular energy storage carrier, lithium-ion battery (LIB) has been widely used in our daily life. With the increase of the application scenarios, the safety of the LIBs receives higher requirements. The charging and discharging processes of the LIBs are usually accompanied by the structure expansion with different degrees. On the one hand, the structure expansion will affect the assembly space of the LIBs, on the other hand, the accumulation of the side reactions caused by the irreversible expansion will also lead to the structural destruction of the active material and
accelerate the capacity fading. For a single cell, there are several methods for characterizing its expansion performance, such as applying a certain pressure on the surface of a single cell, and testing the expansion force or the expansion thickness of the cell. However, the expansion parameters measured by all these methods include the expansion of multiple positive and negative electrodes, separators and aluminum plastic film or aluminum shell, which cannot accurately analyze the expansion property of a material.
Scheme of Model Coin Cell

Main features:
1.The instrument size is small (length * width * height 120 * 150 * 280mm), which can be placed in the glove box;
2.The model coin cell can be used to assemble various types of full coin cell;
3.Good tightness can ensure long-term test stability and obtain more reliable test results;
4.High-precision thickness measurement system, thickness measurement resolution 0.1µm, precision ± 1 µm.
5.In-situ test of the full-cell expansion thickness curve;
6.Ion conductivity of the solid electrolyte can be measured;
7.The software can automatically combine the thickness change of the model coin cell with the
charging and discharge data (compatible with partial charging and discharge tester), and outputthe report involving all testing data.
Application case

1.NCM-Graphite Full Coin Cell:
Assemble the NCM-Graphite LIB to test the thickness change during charge and discharge; test parameters: the current density is 0.6mA / cm2,2.8~4.2V;
The thickness of the battery decreases in the first charing process, which is mainly due to the rest stage after assembly.
Under a certain pressure condition, the interface contact between the positive and negative electrodes will gradually get close, so it is necessary to rest as far as possible (usually for more than 3h) before start to measure the thickness expansion during the charging process;
The thickness change of both charging and discharge processes was about 1.33 μm/mAh, along with a corresponding volume change of 0.2 mm3/mAh, which is mainly caused by the deintercalation of the lithium ions from the graphite.
The thickness of the graphite coating is about 100 μm. If ignore the expansion effect of the positive electrode, the percentage of the thickness change of graphite is about 2%.

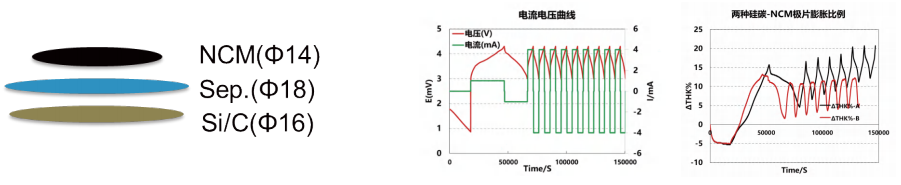
Assemble NCM-Si / C LIB and test the thickness change during charge and discharge; test parameters:
current density is 0.6mA / cm2,3~4.3V;
Ignore the expansion of NCM positive electrode, and the total expansion thickness measured from the model coin cell mainly comes from the expansion of the SiC negative electrode during the expansion experiment. By further deducting the thickness of the copper current collector, the thickness expansion ratio can be calculated;
Compared with two kinds of materials, expansion ratio of A material is greater than that of B material. The expansion ratios of these two materials at the first charging process are similar. During the subsequent cycling, the maximum expansion thickness of B material will decrease compared to the first cycle, and shows increase gradually during the cycling. However, for the A material, the maximum expansion thickness of each cycle increase continuously. These different expansion behaviors between these two materials are due to the different modification ways.
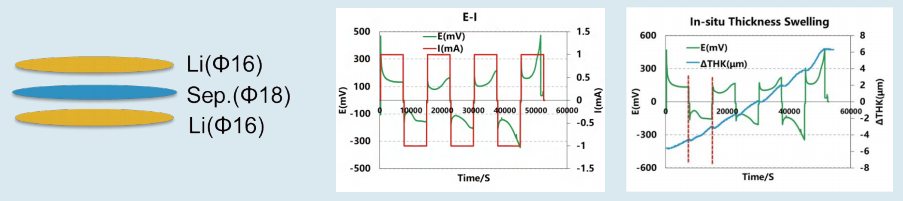
3.The L i-L i Symmetric Cell:
Assemble Li-Li symmetric cell to test the thickness change during lithium deposition; test parameters:
current density is 0.5mA / cm2, charing and discharging for 2h and rest for 5min;
During the lithium deposition, the total thickness of the cell gradually increased. Every 2 mAh of the lithium deposition will cause the increase of the thickness of about 2 μm, corresponding to the volume expansion of about 0.76 mm3/mAh
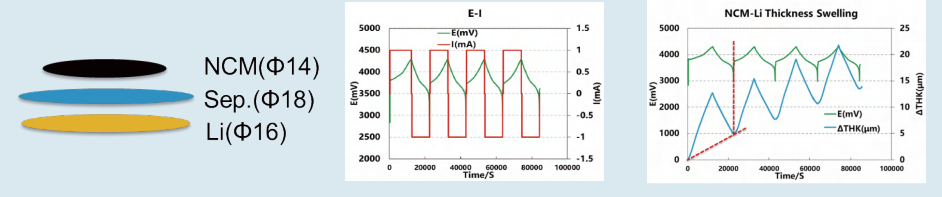
4. NCM-Li half battery:
Assemble the NCM-Li half cell to test the thickness change during charing and discharging; test parameters: the current density is 0.6mA / cm2,3~4.3V;
During the charging process, the thickness expansion is about 4 μm/mAh, and the volume expansion is about (0.6 mm3/mAh), which is mainly caused by the lithium plating at the surface of the lithium metal anode;
During the discharging process, the thickness shrinkage is about 3 μm/mAh, and the volume shrinkage is about (0.5mm3/mAh), which is mainly due to the decrease of the thickness of the lithium metal anode caused by the continuous deintercalation of the lithium ions from the lithium metal anode.
Model
|
Model
|
MCS1000
|
MCS1400
|
|
Number of channels
|
Single channel
|
Four channel
|
Main parameters
|
Thickness measurement range
|
0-10mm
|
|
Thickness resolution
|
0.1um
|
|
Thickness measurement accuracy
|
±1um
|
|
Mold size
|
Inner diameter 13mm, 16mm, 20mm
(other diameters available)
|
Installation conditions
|
Power supply
|
220-240V/50-60Hz
|
|
Voltage change tolerance
|
±10%
|
|
Power consumption
|
30W
|
|
Net weight
|
10kg
|
|
Instrument size
|
120*150*280 mm
|










 en
en fr
fr de
de ru
ru es
es pt
pt ko
ko tr
tr pl
pl th
th







































 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported